
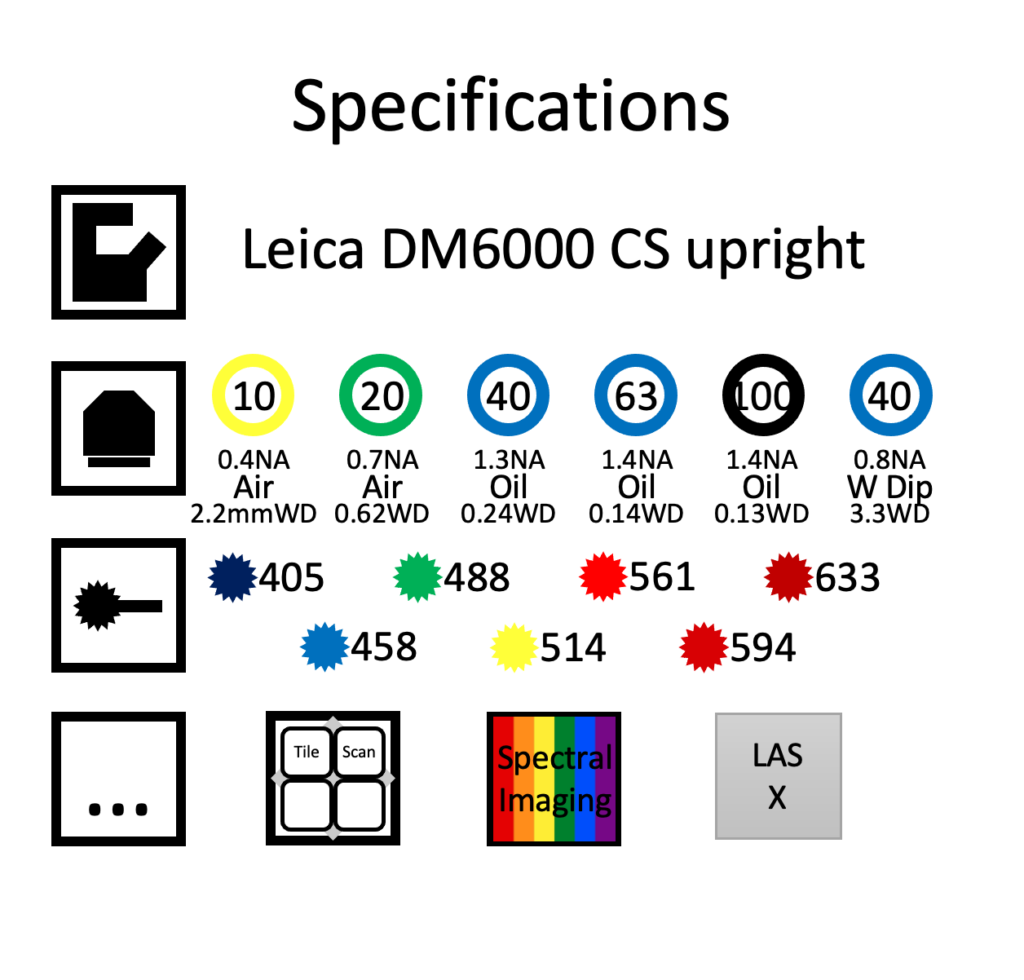
Leica SP8 upright confocal

Technology Focus
Confocal microscopes use a pinhole to reject out of focus light resulting in optical sectioning and an improved signal to noise ratio when compared to widefield fluorescence imaging. (See figure below – only in-focus light can pass through the pinhole to reach the detector).

Confocal microscopes are ideal for imaging multi-labelled fluorescent samples up to around 100 microns in depth.
Figure credit – https://www.edinst.com/

The image above shows an orthogonal view of a mouse kidney section taken using the 60x/1.4 NA oil immersion objective. Nuclei are DAPI labelled and shown in cyan, cell membranes in yellow and actin cytoskeleton in magenta.
